Is A Money Market A Cash Equivalent

Cash and Cash Equivalents are recorded equally electric current assets
Cash and greenbacks equivalents (CCE) are the most liquid electric current avails found on a concern's rest sheet. Cash equivalents are short-term commitments "with temporarily idle cash and easily convertible into a known cash amount".[1] An investment commonly counts as a greenbacks equivalent when information technology has a short maturity period of ninety days or less, and can exist included in the greenbacks and cash equivalents balance from the date of acquisition when it carries an insignificant risk of changes in the nugget value. If information technology has a maturity of more than 90 days, it is not considered a cash equivalent. Equity investments mostly are excluded from cash equivalents, unless they are substantially cash equivalents (e.g., preferred shares with a curt maturity period and a specified recovery date).[ii]
Ane of the visitor's crucial wellness indicators is its ability to generate cash and cash equivalents. Then, a company with relatively high net assets and significantly less cash and cash equivalents can more often than not be considered an indication of not-liquidity. For investors and companies cash and cash equivalents are generally counted to be "low risk and low return" investments and sometimes analysts tin approximate company'due south ability to pay its bills in a short period of time by comparing CCE and electric current liabilities. Nevertheless, this can happen just if there are receivables that tin be converted into cash immediately.[3]
Even so, companies with a big value of cash and cash equivalents are targets for takeovers (past other companies), since their excess cash helps buyers to finance their acquisition. Loftier cash reserves can also indicate that the company is not effective at deploying its CCE resources, whereas for big companies it might be a sign of training for substantial purchases. The opportunity toll of saving up CCE is the return on equity that company could earn by investing in a new product or service or expansion of concern.[4]
Components of cash [edit]
- Currency
- Coins
- Banking company overdrafts commonly are considered as financing activities. However, where banking concern borrowings which are repayable on a demand grade an integral role of company's cash management, banking concern overdrafts are considered to be a part of greenbacks and cash equivalents.[5]
- Cash in saving accounts is by and large for the saving purposes so that they are not used for daily expenses.
- Cash in checking accounts allow to write checks and employ electronic debit to admission funds in the account.
- Money gild is a financial instrument issued past regime or financial institutions which is used past payee to receive cash on demand. The advantage of money orders over checks is that it is more trusted since information technology is always prepaid. They are acceptable for payment of personal or small business's debts and can be purchased for a small fee at many locations such as post part and grocery.[6]
- Fiddling greenbacks is a small-scale amount of cash that is used for payment of insignificant expenses and the amount of it may vary depending on the organisation.[seven] For some entities $50 is adequate amount of cash, whereas for others the minimum sum should be $200. Petty cash funds must be safeguarded and recorded in order to avert thefts. Often there is a custodian appointed who is responsible for the documentation of piffling cash transactions.[eight]
Components of greenbacks equivalents [edit]

1969 $100,000 Treasury Bill
- Treasury bills, also called "T-bills", are a security issued by the U.S. Department of Treasury, where their purchase lends coin to the U.S. government.[9] T-bills are auctioned in denominations of $100, upward to maximum amount of $5 million (or 35% of the auction offering if a competitive bid) and lack a coupon payment, only instead are sold at a discount, their yield being the difference between purchase price and redemption value, which is paid at maturity. Regular series Treasury bills mature in 4, 13, 26 & 52 weeks from their effect appointment, which may exist purchased via TreasuryDirect or a licensed broker. [10] [eleven]
- Commercial paper is a bearer document which is used by big companies. The minimum amount permitted[ by whom? ] is £100,000 and this grade of borrowing is not suitable for sure "entities".[12] Finance companies sell 2/3 of their total commercial paper to the public, just there are also some companies which borrow less and sell their commercial newspaper to "paper dealers" who then re-sell the papers to the investors. A "circular lot" for paper dealers is approximately £250,000.[13]
- Marketable securities brand business look more liquid, since they are also included in the calculation of electric current ratio. These securities are generally traded on public exchange due to their ready price availability.[14] There are two forms of Marketable Securities: Marketable Equity Securities and Marketable Debt Securities.[15]
- Money market funds are like to checking accounts, but they mostly pay higher interest rates generated on deposited funds.[16] Internet asset Value (NAV) of Coin Marketplace funds maintains stable compared to other common funds and its share toll is constant: $1.00 per share. For businesses, not-profit organizations and many other institutions MMF are very constructive "vehicle" for cash management.[17]
- Short-term government bonds are mostly issued by governments to support authorities'due south spending. They are generally issued in country's domestic currency and in the U.S authorities bonds include the Savings bond, Treasury bond, Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities and many others. Before investing into government bail investors should take into account political risk, inflation and involvement rate take a chance.[18]
Calculation of greenbacks and cash equivalents [edit]
Cash and cash equivalents are listed on balance sail equally "electric current assets" and its value changes when dissimilar transactions are occurred. These changes are called "cash flows" and they are recorded on accounting ledger. For case, if a company spends $300 on purchasing goods, this is recorded as $300 increase to its supplies and decrease in the value of CCE. These are few formulas that are used past analysts to calculate transactions related to greenbacks and cash equivalents:
Change in CCE = End of Year Cash and Cash equivalents - Beginning of Yr Cash and Cash Equivalents.[19]
Value of Cash and Cash Equivalents at the cease of period = Net Cash Flow + Value of CCE at the period of beginning [20]
Liquidity measurement ratios [edit]
Restricted cash [edit]
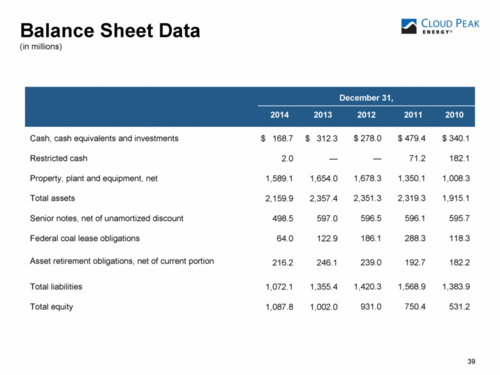
How Restricted Cash is presented in a balance sheet
Restricted greenbacks is the corporeality of cash and cash equivalent items which are restricted for withdrawal and usage. The restrictions might include legally restricted deposits, which are held as compensating balances against curt-term borrowings, contracts entered into with others or entity statements of intention with regard to specific deposits; nevertheless, fourth dimension deposits and brusk-term certificates of deposit are excluded from legally restricted deposits. Restricted cash can exist also fix bated for other purposes such as expansion of the entity, dividend funds or "retirement of long-term debt". Depending on its immateriality or materiality, restricted greenbacks may be recorded as "greenbacks" in the financial argument or it might exist classified based on the date of availability disbursements. Moreover, if cash is expected to be used within one twelvemonth afterwards the balance sheet engagement it tin be classified as "current asset", but in a longer period of time information technology is mentioned equally not- current nugget. For example, a large machine manufacturing company receives an accelerate payment (eolith) from its customer for a automobile that should be produced and shipped to another land within 2 months. Based on the customer contract the manufacturer should put the deposit into separate bank account and non withdraw or use the money until the equipment is shipped and delivered. This is a restricted cash, since manufacturer has the eolith, simply he tin can not use it for operations until the equipment is shipped.
Run across also [edit]
- Residual sail
- Currency
- Inflation
- Inflation hedge
- United States Treasury security
References [edit]
- ^ Hermanson, Roger (1998). Accounting A Concern Perspective. USA: McGraw-Hill. pp. 150. ISBN0-256-16732-X.
- ^ Denis, Durant (22–23 January 2013). "IAS 7 Statement of Greenbacks Flows- identification of greenbacks equivalents" (PDF). IFRS. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 May 2016. Retrieved 2 Nov 2015.
- ^ "What are greenbacks and cash equivalents? - Questions & Answers - AccountingTools". www.accountingtools.com . Retrieved 2015-11-03 .
- ^ "Cash and Greenbacks Equivalent". www.accountingsoul.com . Retrieved 2015-11-04 .
- ^ "Set up for IFRS: The Components of Greenbacks and Cash Equivalents (IAS 7)". faainc.blogspot.co.uk. April 2010. Retrieved 2015-eleven-03 .
- ^ "ICI - Money Marketplace Funds: FAQs". world wide web.ici.org . Retrieved 2015-eleven-05 .
- ^ Nobes, Christopher (2006). Penguin Dictionary of Bookkeeping. London: Penguin Books. p. 227. ISBN978-0-14-102525-4.
- ^ "Piffling Cash Definition | Investopedia". Investopedia . Retrieved 2015-eleven-05 .
- ^ "How Treasury Bills Work". HowStuffWorks. 16 July 2008. Retrieved 2015-11-04 .
- ^ "Individual - Treasury Bills In Depth". www.treasurydirect.gov . Retrieved 2020-07-11 .
- ^ "Treasury Nib (T-Bill) Definition | Investopedia". Investopedia . Retrieved 2015-11-04 .
- ^ Dyson, John (2007). Bookkeeping for Non-Accounting Students. London: Pearson. p. 436. ISBN978-0-273-70922-0.
- ^ "Commercial Paper". cucfa.org . Retrieved 2015-11-04 .
- ^ "Marketable Security Definition - AccountingTools". www.accountingtools.com . Retrieved 2015-11-04 .
- ^ "Marketable Securities". www.coin-zine.com . Retrieved 2015-eleven-04 .
- ^ "Money Market Fund Definition | Investopedia". Investopedia . Retrieved 2015-11-04 .
- ^ "ICI - Money Market Funds: FAQs". www.ici.org . Retrieved 2015-11-04 .
- ^ "Government Bond Definition | Investopedia". Investopedia . Retrieved 2015-eleven-04 .
- ^ "What Is Included in a Cash & Cash-Equivalent Calculation Statement?". Small Business organization - Chron.com . Retrieved 2015-11-04 .
- ^ "What Is Included in a Greenbacks & Cash-Equivalent Calculation Statement?". Small Business - Chron.com . Retrieved 2015-11-04 .
- ^ "Liquidity Measurement Ratios: Current Ratio | Investopedia". Investopedia . Retrieved 2015-11-05 .
- ^ "Liquidity Measurement Ratios: Quick Ratio | Investopedia". Investopedia . Retrieved 2015-eleven-05 .
- ^ "Quick ratio".
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cash_and_cash_equivalents
Posted by: harbershonserema.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Is A Money Market A Cash Equivalent"
Post a Comment